Mixing, casting and advantages of GRC (GFRC)
The following is a concise account of the essential features of Glassfibre Reinforced Concrete or GRC (GFRC). It is an overview. Further details can be found in the Downloads or via the Links
KEY CONCEPTS
Not limited to, but, in principle*, GRC consists of 2->5% by weight of AR glassfibres typically blended into a 1:1 cement: sand and water mix to produce a new, high strength concrete – GRC (or GFRC). GRC has good compressive, tensile and bending strength so products can be designed thinner [6-30mm] with greatly reduced weight (3-8 times lighter).
AR glassfibres do not corrode like steel and act like 1000’s of tiny reinforcing bars randomly distributed throughout the cement mix.
Generally, AR glassfibres are used in the production of thin [6-30mm], precast, factory-finished, quality concrete not heavy products such as blocks, paving slabs, or pipes.
*Admixtures can change this basic information
ADVANTAGES OF GRC
- Reduced product weight (24kg/m2 at typical 12mm. thickness).
- Reduced transport and installation costs.
- Reduced loading on buildings and foundations.
- Excellent edge and corner strength.
- Ability to reproduce fine surface detail and quality of finish.
- Easy to mould into complex shapes.
- Maintenance free (no steel to corrode).
- Excellent fire properties
- Excellent freeze/thaw resistance
- Not affected by UV
- Neither Uses nor emits volatiles and is a low energy product
“GRC provides the specifier with an end-product range that few other materials can match”
RAW MATERIALS FOR GRC
- Alkali resistant (AR) glassfibre formed into continuous strands or mesh or pre-chopped strands.
- Portland cement, white or grey (with or without pigments) plus rapid-setting cement.
- Clean, dry and graded sand.
- The acrylic polymer as a mixing aid and for curing and improved properties.
- Water.
- Admixtures to improve properties or mould filling
TYPICAL FORMULATION
|
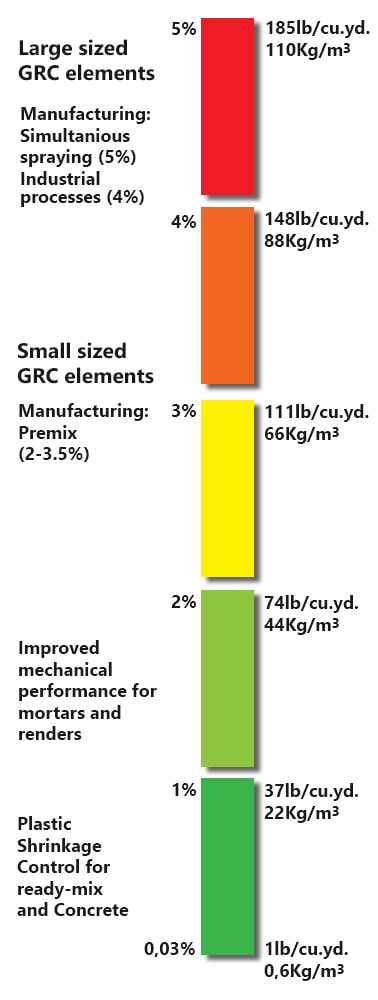 % Fibre versus Applications
|
*If more sand is added, the bond to the fibre is reduced resulting in a significant loss of strength.
MIXING INSTRUCTIONS
Mortar mix
Blend the water, polymer and plasticiser (if used) together. Add the sand. Start mixer, add cement and blend until lump free.
Blending in the fibre
The fibres are added depending on the production process being used. The 2 common methods are:
- Premix using pre-chopped 6 or 12mm fibre
- Chopping/Spraying process with purpose-built equipment.
Premix

Chopped AR fibre strands
The chopped strands are simply stirred into the mortar mix until they are dispersed with no dry clumps visible usually 1-2min.
Special mixing equipment can be used but both polymer and modern admixtures mean that many standard mixers can also now be used successfully [but always check the flexural strength of the cured GRC to confirm this
Chopping/Spraying
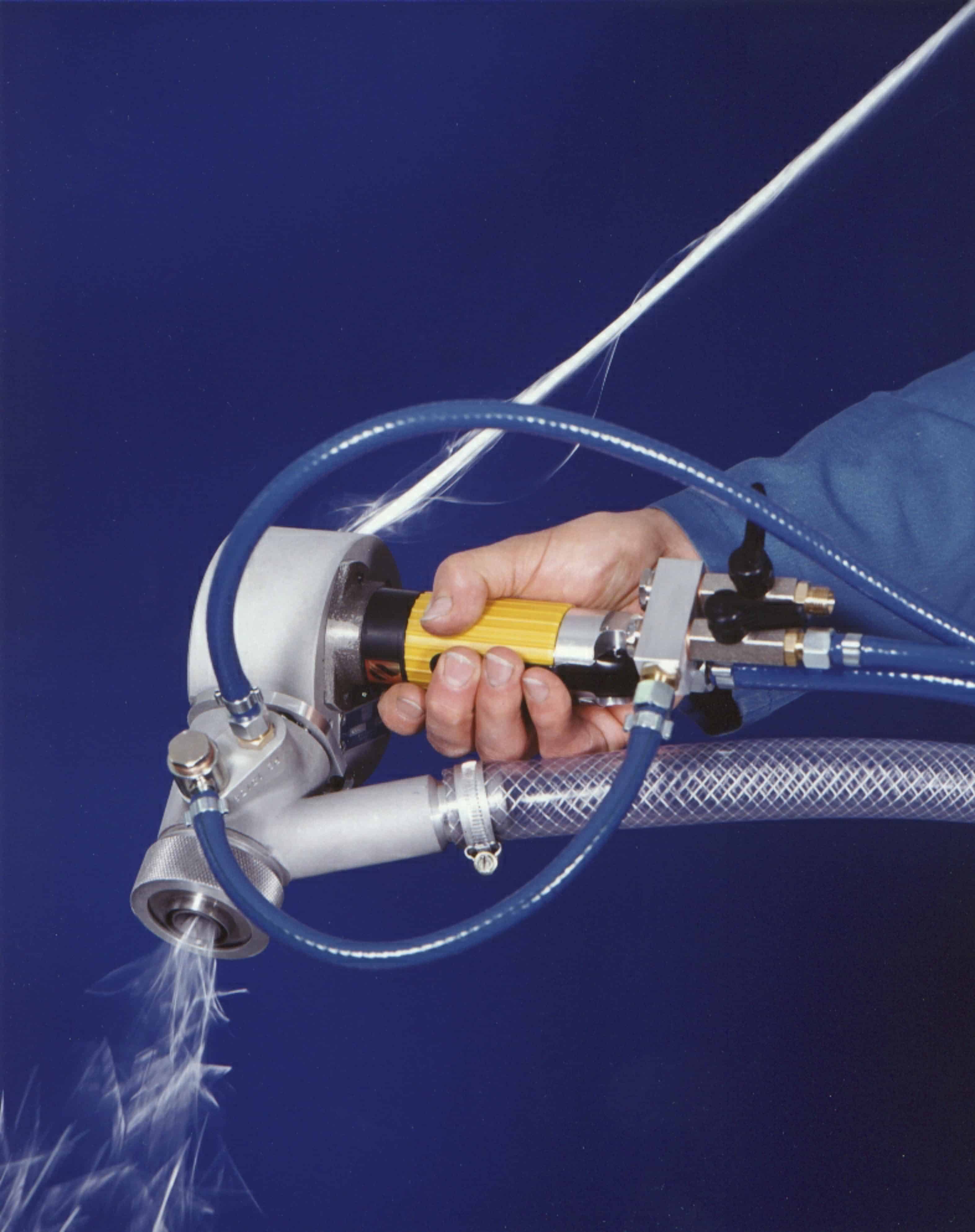
In purpose made equipment, the wet mortar is pumped to the spray head and atomised by air pressure. The continuous strands are fed into a chopper gun, cut to 25- 35mm and simultaneously sprayed out with the wet mortar directly onto the mould. This fibre/mortar mix then has to be compacted with rollers

Dual Premix & simultaneous spray pump
MOULDS FOR GRC
The appearance of the finished product is influenced by the mould material and the quality of the mould itself.
Moulds can be made from various materials such as:-
- Steel
- Plywood
- Plastic
- Glassfibre reinforced resins
- GRC itself
- Rubber moulding compounds
A combination of materials is frequently necessary in order to give the desired stiffness, shape and surface finish.
All corners should have fillets, chamfers or rounded corners and mould release compounds to match the mould material being used.
FINISHES FOR GRC
Basic finishing techniques:
- Mist Coats
- Face mixes
- Coatings
Mist Coat
1-3 mm layer of the sand/cement mix [no fibre] is first sprayed into the mould and allowed to ‘firm-up’ before the fibrous GRC mix is applied. The appearance can be enhanced by acid etching or light sanding or abrasive blasting after demoulding.
Face mixes
A 4-6mm. thick cement/sand or crushed stone, pigmented mix is laid into the mould before the GRC backing is applied. The facing mix can be left ex-mould or, more usually, exposed by either:
- using chemical retarders placed on the mould then washing after demoulding.
- by acid etching after demoulding.
- by mechanical exposure through abrasive blasting
- honing and polishing with diamond disks.
Coatings, paints and penetrating stains

Bespoke Fencing Murial
GRC is a dense, smooth surface and coating manufacturers should be consulted. The surface should be lightly sand blasted or acid etched to improve adhesion and should be of the ‘breathing’ type.
NOTE
There are MANY “secrets of the trade” which can be used to enhance the appearance of the finished produce



